State-mandated retirement plans are gaining momentum across the U.S. Every year, more states are adopting mandated retirement plans, either in the pilot phase or further, requiring companies of certain sizes to automatically enroll employees in an IRA or another qualifying private plan.
But what exactly is a state retirement plan? How do state-mandated retirement plans work? And which states have mandated retirement plans? Read on to discover the answers to these questions and more.
Retirement Plan Mandates Are Becoming a Reality for These 15 States:
California, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Illinois, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, Oregon, Vermont, Virginia, and Washington.
While federal retirement plan mandates are still a long way off, 20 U.S. states have enacted state-sponsored retirement savings programs, 13 of which are open to eligible employers and workers and are required by law.
As of January 1, 2025, 13 of the 20 state programs (11 Auto IRA: CA, CO, CT, DE, IL, MD, ME, NJ, OR, VA, VT) and 2 others—MA (MEP) and WA (Marketplace)—are open to all eligible employers and workers.
While this is an important step toward addressing the retirement gap and its impact on the private sector, what does it mean for business owners?
Depending on where your business operates, there are specific retirement plan adoption deadlines that your company will need to meet to continue operating legally and avoid penalties. To help you navigate these mandates, we’ve broken them down by state.
First up: Are retirement plans mandatory in California for all companies?
California
California launched its state-sponsored retirement plan, CalSavers, in 2016, allowing companies to choose between a Roth IRA or a Traditional IRA for employees.
Timeline
On June 30th, 2022, all California businesses with five or more employees are required to enroll in CalSavers or a qualified plan. On August 26th, 2022, Governor Gavin Newson expanded CalSavers to include all employers with at least one eligible employee.
- Registration Deadline: Employers have 1+ employees by December 31, 2025, or offer a qualifying alternative that meets the state mandate.
Penalties
If California enterprises fail to comply, they will be fined $250 per eligible employee if non-compliance continues for 90 days or more after the notice, $500 per eligible employee if non-compliance continues for 180 days or more after the notice, and $500 per employee for each subsequent year and any non-consecutive year of noncompliance. These penalties will be collected by the CA Franchise Tax Board.
Colorado
Timeline
Colorado’s mandated retirement savings program, Colorado Secure Savings Program, has been active since 2023.
- Registration Deadlines: Employers with 5+ employees must register for the Colorado Secure Savings Program by May 15 of the year after meeting the employer requirements.
The mandate applies to any Colorado company without an existing plan that employs five or more employees and has been in operation for at least two years. Employer contributions, and their resulting tax benefits for companies, are not permitted unless a qualifying private plan is adopted.
Penalties
Non-compliant employers face fines of up to $100 per unenrolled eligible employee annually, with a maximum penalty of $5,000 per calendar year. Penalties are enforced by the Colorado Department of Labor and Employment (CDLE).
Connecticut
Timeline
The law establishing Connecticut’s state-sponsored retirement plan, MyCTsavings, was passed in 2016. Participants can choose between a Roth IRA or a Traditional IRA, both funded through payroll deductions. The program applies to any employer who paid at least $5,000 in wages the preceding year.
MyCTSavings exited its pilot phase on March 24, 2022, and is now fully operational. It is overseen by a state-appointed board to assist employees who lack access to an employer-sponsored retirement plan.
- Registration Deadline: Employers must register if they have 5 + employees by August 31 of each year after meeting the eligibility criteria.
Penalties
Eligible employers who fail to enroll in MyCTSavings or a qualifying plan by the deadline may face civil action.
Delaware
Timeline
Delaware launched its state-sponsored retirement plan, Delaware EARNS, in 2022. Passed by the Delaware General Assembly and signed into law by the Governor, EARNS promotes individual retirement savings. Employees are automatically enrolled in a Roth IRA but may opt-out.
Employers required to participate should have received prior notifications. The deadline for newly eligible businesses to sign up or certify an exemption was October 15, 2024. The deadline passed! Don’t wait and act now.
Registration Deadline– Employers are required to register if they:
- Have 5 + employees
- Have been in business since July 1 of the previous year
- Do not offer a qualified retirement plan
Penalties
Non-compliant employers face fines of $250 per unenrolled eligible employee, with a maximum penalty of $5,000 per calendar year.
Hawaii
The Hawaii Retirement Savings Program requires employers to automatically enroll employees into a payroll deduction IRA if they do not offer a qualifying plan. Employees can opt out at any time.
Timeline
The bill passed in May of 2022. While Act 296 took effect in July 2022, the Hawaii Retirement Savings Board has yet to implement the program.
Penalties
If eligible employees are not automatically enrolled, employers must:
- Deposit the amount that would have been made by the employee into the employee’s account (interest rates apply).
- Pay a penalty of $25 for each month the covered employee was not enrolled in the program and,
- $50 for each month the eligible employee continues to be unenrolled after the penalty has been given.
Illinois
Timeline
Illinois’ state-mandated retirement plan, Secure Choice, was enacted in 2015 and administered by the Illinois Secure Choice Savings Board.
- Current Registration Deadline: Employers with 5+ employees must register by February 28 of each year.
Penalties
Companies that do not enroll in Illinois Secure Choice or a qualifying private plan will face a penalty of $250 per employee for the first year, and $500 per employee for each following year. Penalties will be collected by the IL Dept. of Revenue (IDOR).
Maine
The state-sponsored program, overseen by the Maine Retirement Savings Board, is a payroll deduction Roth IRA that must be offered by any individual or entity engaged in business in the state of Maine that has been active for at least two years. All Maine employers that have been in business for two years and have five or more covered employees—employees who are 18 or older and have a social security number—are required to register with MERIT.
Timeline
Businesses are reviewed for eligibility annually based on the past year. So if you had four employees in 2023, but employed five or more in 2024, you are required to register with MERIT in 2025. Employers may opt out of the state-sponsored program if they offer another qualifying plan.
- Businesses notified before January 1, 2025- Your registration deadline has passed
- Newly eligible businesses 5+ employees must register by June 30, 2025
Penalties
The penalties for non-compliance prior to April 1, 2024, is a maximum $10 per employee. Between April 1st, 2024, and March 31st, 2025, the maximum fine per employee will be $20. From April 1, 2025, to September 30th, 2026, the maximum penalty per employee goes up to $50. On or after Oct. 1, 2026, the tier goes up to $100. These dates are still subject to change.
Maryland
Timeline
Maryland$aves the state’s mandated retirement program, was enacted in 2016 and launched to employers in September 2022. Before opting into Maryland$aves, be sure to explore all options as a Roth IRA may not be right for all businesses.
- Registration Deadline: Employers with 1+ employees must register by December 31 of each year.
Penalties
Currently, there are no penalties for non-compliance.
Massachusetts: Voluntary
Since most small non-profits cannot afford to offer retirement benefits, Massachusetts introduced the Massachusetts CORE Plan. This plan is reserved for non-profits with 20 or less employees. Employers that enroll their non-profit in this plan will auto-enroll their employees after 60 days, however, employees may opt out at any time. This retirement plan is funded using pre-tax dollars.
Timeline
This program is available now. Massachusetts has also looked into expanding this program to all businesses with more than 25 employees, however, this legislation has not passed as of yet.
Penalties
Because the system is opt-in, employers of non-profits will not be punished for not joining the state’s plan or offering a qualifying plan.
New Jersey
Timeline
New Jersey’s Secure Choice Savings Program, enacted in 2019, requires businesses with 25+ employees to either opt into the state-sponsored Auto IRA retirement plan or offer a qualifying private plan.
Per the original bill, the program was to become effective on March 28, 2021, with the objective of enrolling everyone by the end of 2021. The program now called RetireReady NJ, delayed due to the pandemic, will open fully on June 30, 2024. Employers with 40+ employees must register by September 15, 2024, and those with 25-39 employees by November 15, 2024. The deadline has passed, so take action today!
Registration Deadline: Employers must participate if they have:
- 25 + employees (as of the previous calendar year)
- Been in business for at least two years
- Not offered a qualified retirement plan in the past two years.
Penalties
If an employer does not comply by the first year, they receive a written warning from the state; the second year, they are fined $100 per employee not enrolled; the third and fourth year, they are fined $250 per employee not enrolled; the fifth year onward, they are subject to a $500 fine per employee not enrolled in the program. Those fines increase for any employer who collects employee contributions.
New Mexico: Voluntary
New Mexico’s state-run program is the most unique so far. For one, it is not a mandate but created so employers and employees can opt-in to a plan should they want one. Secondly, it has been instituted as both a retirement marketplace and a Roth IRA. What this means is employers and employees have the option to join the Roth IRA or “shop” for other options on the New Mexico retirement marketplace.
Timeline
Originally set for early 2021, the program has been delayed. The implementation deadline is now set for July 1, 2024, though no new date has been set.
Penalties
Because the system is opt-in, employers will not be punished for not offering a qualifying plan. However, the state-administered Roth IRA may not suit the needs of every business in New Mexico.
New York
New York’s Secure Choice Savings Program was originally enacted in 2018 and is an Auto IRA plan. Looking forward to 2025, businesses with 10 or more eligible in-state employees at all times during the previous calendar year are considered covered businesses and must participate in the New York state’s Secure Choice Savings Program or offer a retirement plan that satisfies the mandate. Employees will be auto enrolled and have the option to opt out.
Timeline
New York City’s program will no longer be implemented because New York State enacted an Auto IRA program and New York City would now become part of the state program.
Businesses must register within nine months after the program’s official launch, which is scheduled for late 2025 following a pilot this summer.
Penalties (TBD to Pilot and Launch)
Businesses that do not enroll will face a penalty of $250 per employee for the first year, and $500 per employee for each following year, and the fines go up from there for each consecutive year of non-compliance.
Oregon
Oregon also requires employers to offer retirement plans to employees, be it through their state-sponsored plan, OregonSaves, or a private qualifying plan. The state does not require employer contributions.
Timeline
The program has been implemented in six phases, starting with businesses having the largest number of employees.
- Registration Deadlines: 1+ employees must register by July 31 of each year
Penalties
If a company is cited for non-compliance, it must pay a fine of $100 per affected employee, up to a maximum of $5,000 per calendar year.
Vermont: Voluntary
Timeline
Vermont has changed its state program from a voluntary MEP enacted in 2017 to an Auto IRA program in 2023. The Vermont Saves Pilot Program, launched in partnership with Colorado, began in October 2024 and opened fully in December 2024.
- Registration Deadline: Employers with 5+ employees must register by March 1, 2025.
Penalties
Prior to October 1, 2025, the penalty will cost $10 per employee. Following in October 1, 2025 – September 30, 2026, it will cost $20 per employee. Lastly, on or after October 1, 2026, it will cost $75 per employee.
Virginia
Timeline
Virginia’s state-administered retirement plan program, RetirePath, is a Roth Individual Retirement Account (IRA) that just launched in June 2023.
- Registration Deadline: Employers with 25+ employees must register by October 30 of each year.
Penalties
Employers who do not offer retirement options for their employees face a penalty of $200 per eligible employee per year.
Washington: Voluntary
Timeline
The city of Seattle enacted its mandatory retirement savings program in 2017, which is overseen by the mayor.
In 2018, officials delayed the implementation of the program pending possible action by the Washington State Legislature on a statewide Auto IRA program. As of 2022, Seattle’s retirement mandate has still not been implemented.
However, Washington State has implemented a retirement plan marketplace. Retirement plan marketplaces allow each employee to take charge and choose the IRA that is right for them. Employers do not have to sponsor the plan for the employees directly, as each employee can voluntarily contribute to their retirement account through the retirement marketplace.
Looking Forward
In March 2024, the governor signed into law the Washington Saves retirement program for private-sector employees. By July 1, 2027, all private employers who have been in operation for at least two years in the state and have a workforce that has combined for at least 10,400 hours the previous calendar year must participate in the Auto IRA program unless they offer an alternative plan that satisfies the mandate.
Penalties
Due to the current program being voluntary, there are no penalties for non-participation.
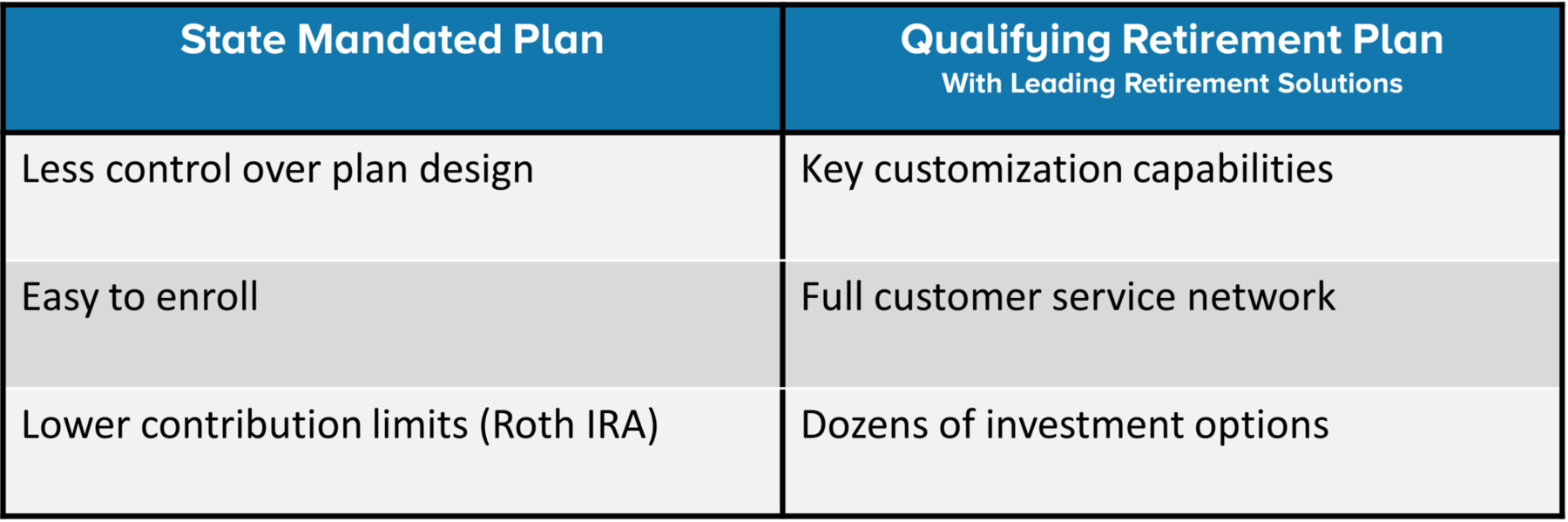
A Retirement Plan Built for Your Business
If your state has not instituted a retirement plan, or your looking for a plan that is designed around your business needs, we’ve got the solution:
Connect with us on Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter!
For tips and information regarding retirement plans, contact us.









